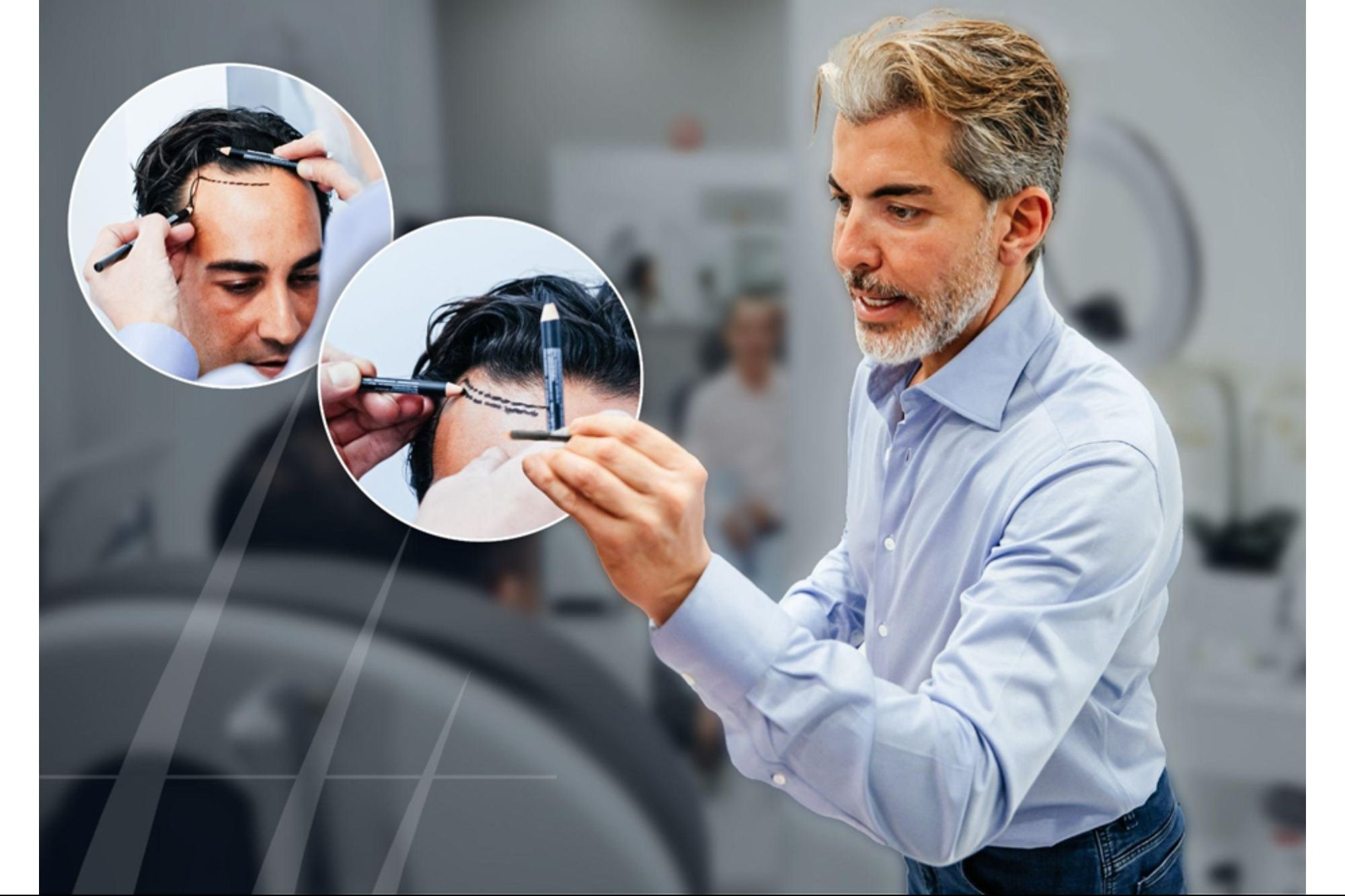
Hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, causing not just physical changes but often significant psychological and emotional impacts. While traditional treatments have existed for decades, recent years have witnessed remarkable technological advancements that are revolutionizing the field of hair restoration. These cutting-edge innovations offer more effective, less invasive, and more natural-looking solutions than ever before. This comprehensive guide explores the latest breakthroughs in hair restoration technology, providing insights into how these advancements are transforming outcomes for those experiencing hair loss.
Understanding Modern Hair Loss Solutions
Before diving into specific technologies, it’s important to understand the evolution of hair restoration approaches and how modern solutions differ from their predecessors.
The Evolution of Hair Restoration
Hair restoration has undergone dramatic transformation since its early days:
- 1950s-1980s: Large “plug” grafts resulting in unnatural “doll’s hair” appearance
- 1990s-2000s: Mini/micro-grafting techniques improved aesthetics but were labor-intensive
- 2000s-2010s: Introduction of Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
- 2010s-Present: Advanced automation, robotics, genetic therapies, and regenerative approaches
Modern solutions focus not just on replacing lost hair, but on natural-looking results, minimizing recovery time, reducing scarring, and addressing the biological factors that cause hair loss.
The Multi-Modal Approach
Today’s most effective hair restoration strategies often combine multiple complementary technologies:
- Surgical techniques for immediate visible improvement
- Pharmaceutical treatments to maintain existing hair and support new growth
- Energy-based therapies to stimulate follicular activity
- Regenerative medicine to enhance treatment outcomes
- Scalp care protocols to optimize the environment for hair growth
This comprehensive approach recognizes that hair loss is a complex condition requiring targeted intervention on multiple fronts.
Advanced Surgical Techniques
Surgical hair restoration has been transformed by precision technologies that allow for more natural results with less trauma and downtime.
ARTAS Robotic Hair Transplantation
The ARTAS system represents a significant leap forward in FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) technology:
How It Works:
- AI-powered imaging system identifies and maps optimal donor follicles
- Robotic arm extracts individual follicular units with precise depth control
- Minimizes damage to follicles during extraction
- Creates recipient sites according to pre-designed templates
Benefits:
- Reduces human fatigue factor in lengthy procedures
- Consistent graft quality regardless of procedure duration
- Minimizes transection (cutting) of hair follicles
- Precise harvesting results in less noticeable donor area
Limitations:
- Higher cost than manual FUE procedures
- Currently optimized primarily for straight hair types
- Still requires skilled physician oversight for optimal results
HARRTS (Hair Follicle Replicating and Regeneration Technology System)
This emerging system builds upon robotic FUE with additional automation:
How It Works:
- Combines follicular extraction, preservation, and implantation in one integrated system
- Uses pneumatic controls for gentle handling of grafts
- Computerized implantation ensures consistent depth and angle
- Monitors tissue conditions in real-time during the procedure
Benefits:
- Reduced graft exposure time increases survival rates
- More consistent angulation of transplanted follicles
- Potential for faster procedures with less trauma
- Standardized results less dependent on technician skill
No-Shave FUE Techniques
Traditional FUE required shaving the donor area, but advanced techniques now allow for extraction without visible hair loss:
How It Works:
- Long hair is parted in micro-sections to access the follicular base
- Specialized extraction tools remove follicles while preserving surrounding longer hairs
- Extractions are dispersed to prevent noticeable thinning
- Recipient sites are created to accommodate grafts without shaving recipient areas
Benefits:
- Patients can return to work without visible signs of procedure
- Particularly valuable for women and those who maintain longer hair
- Psychological benefit of avoiding the “surgical look” during recovery
- Can be performed in multiple sessions without social downtime
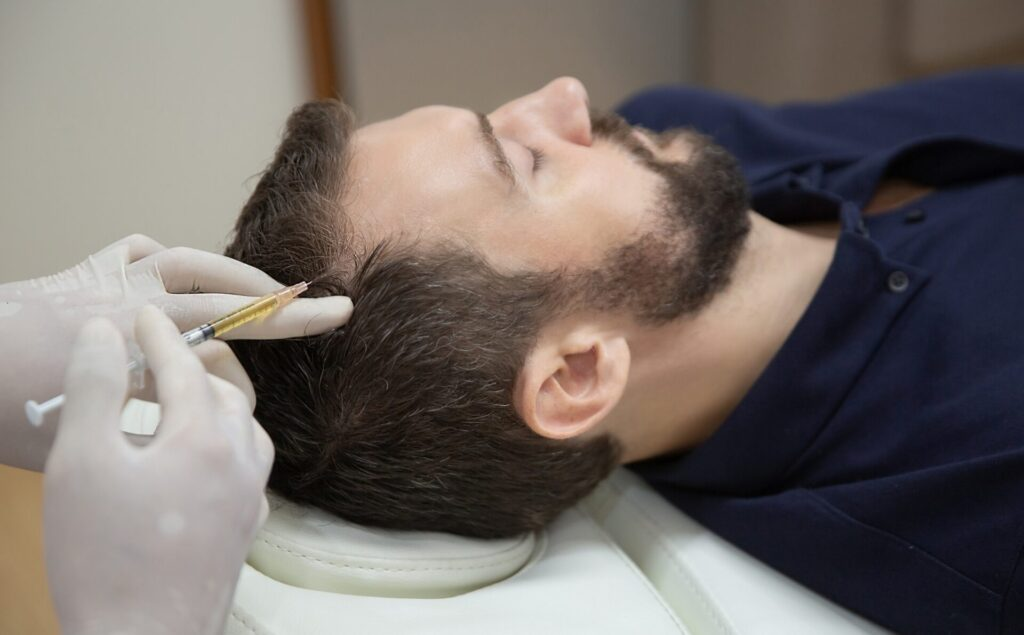
Regenerative Medicine Approaches
Perhaps the most exciting frontier in hair restoration involves harnessing the body’s own regenerative capabilities.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Advancements
While basic PRP has been used for hair restoration for several years, new protocols have enhanced its effectiveness:
Latest Innovations:
- Growth factor isolation: Techniques that concentrate specific growth factors most beneficial for hair follicles
- Combination protocols: PRP combined with microneedling, low-level laser, or exosomes
- Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A second-generation platelet concentrate with prolonged release of growth factors
- Customized preparation: Tailoring platelet concentration based on individual platelet counts and quality
Clinical Applications:
- As a standalone treatment for early hair thinning
- Complementary therapy before and after transplantation to improve graft survival
- Maintenance therapy to enhance pharmaceutical treatments
- Treatment for specific conditions like alopecia areata
Exosome Therapy
Exosomes represent one of the newest frontiers in regenerative hair treatments:
How It Works:
- Exosomes are extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells
- These nano-sized particles contain growth factors, mRNAs, and signaling proteins
- When applied to the scalp, they facilitate cell-to-cell communication
- This communication helps reactivate dormant hair follicles and improve follicular function
Current Research Status:
- Early clinical studies show promising results for hair density and thickness
- Research suggests exosomes may be more potent than traditional PRP
- Laboratory evidence indicates they can stimulate hair follicle stem cells
- Current protocols typically involve microneedling-assisted delivery
Stem Cell Therapy for Hair Regeneration
Stem cell approaches aim to fundamentally restore lost follicular function:
Methods Being Researched:
- Adipose-derived stem cells: Harvested from fat tissue and processed to isolate regenerative cells
- Follicular stem cell isolation: Extracting and multiplying cells from a patient’s own functioning follicles
- Cell culture techniques: Expanding harvested cells in laboratory conditions
- Follicular neogenesis: Creating entirely new hair follicles in previously bald areas
Current Status:
- Several clinical trials underway globally
- Early results show promise for both androgenetic alopecia and scaring alopecias
- Regulatory approval varies significantly by country
- Commercial treatments emerging in some markets, though many experts urge caution
According to medical advancements reported by leading hair restoration specialists, these regenerative approaches represent a fundamental shift from simply redistributing existing hair to actually stimulating new growth and revitalizing dormant follicles.

Energy-Based Technologies
Various forms of energy delivery systems have demonstrated efficacy in stimulating hair growth, either as standalone treatments or complementary therapies.
Advanced Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
LLLT has evolved significantly beyond basic laser combs:
Latest Technology:
- Full-coverage helmets with optimal wavelength combinations
- Programmable treatment protocols based on hair loss pattern
- Portable, rechargeable designs improving treatment compliance
- Pulse-wave technology that may enhance cellular response
Clinical Evidence:
- Multiple randomized controlled trials demonstrating efficacy
- FDA clearance for certain devices for both men and women
- Evidence of cumulative effect with consistent long-term use
- Particularly effective for maintaining results after other treatments
Radio Frequency (RF) Microneedling
This dual-action technology combines two proven hair growth stimulators:
How It Works:
- Microscopic needles create controlled microinjuries to the scalp
- Simultaneously, radio frequency energy is delivered into the dermis
- The combination stimulates wound healing factors and increases blood flow
- Enhanced production of collagen and growth factors supports follicular health
Treatment Protocol:
- Typically requires 3-6 monthly sessions
- Minimal downtime compared to more invasive procedures
- Often combined with topical growth factors or PRP for enhanced results
- Maintenance treatments recommended every 6-12 months
Photobiomodulation Combined Therapy
This approach integrates multiple light wavelengths with complementary technologies:
Components:
- Red and near-infrared light to stimulate cellular energy production
- Blue light to control inflammation and scalp microbiome
- Optional ultrasonic or electrical stimulation channels
- Temperature regulation to optimize blood flow
Application:
- Professional clinic-based systems for intensive treatment
- Home-use devices for maintenance between professional sessions
- Protocols customized to specific hair loss patterns and causes
- Often incorporated into comprehensive treatment plans
Pharmaceutical and Topical Innovations
While minoxidil and finasteride have dominated the pharmaceutical hair loss market for decades, new formulations and compounds are expanding treatment options.
Next-Generation Growth Stimulators
Several new compounds show promise for stimulating hair growth:
Emerging Treatments:
- Prostaglandin analogues: Building on the observation that certain glaucoma medications increase eyelash growth
- Androgen receptor targeting compounds: More selective than finasteride with potentially fewer side effects
- JAK inhibitors: Originally developed for autoimmune conditions, showing promise for various types of alopecia
- Topical finasteride formulations: Designed to provide local action with reduced systemic absorption
Delivery System Innovations:
- Liposomal encapsulation for improved penetration
- Microemulsion carriers that enhance absorption
- Time-release formulations for sustained activity
- Combination delivery systems incorporating multiple active ingredients
Peptide Therapies
Specialized peptides can influence hair growth through various mechanisms:
How They Work:
- Stimulating specific growth factors that support follicle function
- Improving blood flow to follicles through vascular signaling
- Reducing inflammation that contributes to follicular miniaturization
- Inhibiting enzymes involved in androgen metabolism
Current Status:
- Several peptide-based products already on the market
- Ongoing research to identify more potent peptide combinations
- Emerging evidence supporting efficacy as complementary treatments
- Potential for customized peptide formulations based on individual needs
Topical RNA Interference Technology
This cutting-edge approach targets the genetic mechanisms of hair loss:
Mechanism:
- Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) or microRNAs (miRNAs) delivered topically
- These molecules can temporarily suppress specific genes involved in hair loss
- Targets include androgen receptors or inflammatory mediators
- Potentially more selective than traditional pharmaceutical approaches
Development Status:
- Currently primarily in research and early clinical trial stages
- Challenges include effective delivery across the skin barrier
- Promising laboratory results showing modulation of key hair growth pathways
- Potential for highly targeted treatment with minimal systemic effects
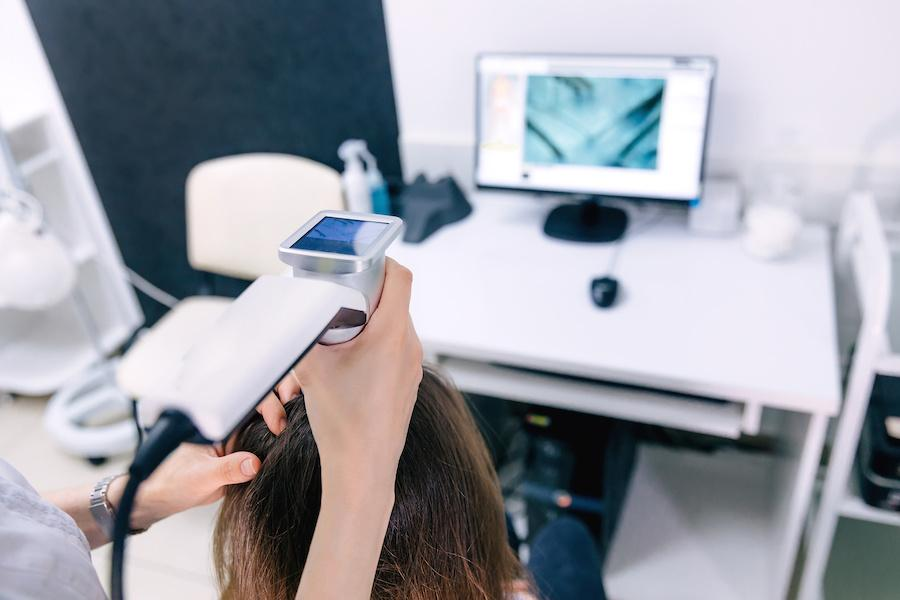

Diagnostic and Monitoring Technologies
Advanced hair restoration increasingly begins with sophisticated diagnostics that allow for personalized treatment planning.
AI-Powered Hair Analysis
Artificial intelligence is transforming how hair loss is assessed and monitored:
Capabilities:
- Precise hair count and density measurements
- Detection of miniaturization before visible thinning occurs
- Tracking of subtle changes over time
- Prediction of progression patterns based on multiple factors
Applications:
- Establishing baseline measurements before treatment
- Objective monitoring of treatment response
- Early intervention based on predictive analytics
- Treatment customization based on specific loss patterns
Genetic Testing for Hair Loss
Genetic analysis provides insight into individual risk factors:
What’s Being Tested:
- Androgen receptor sensitivity variants
- 5-alpha reductase activity markers
- Inflammatory response tendencies
- Multiple gene panels associated with various forms of hair loss
Clinical Utility:
- Predicting likely progression patterns
- Identifying optimal treatment approaches
- Determining risk/benefit ratios for specific interventions
- Personalizing preventative strategies
Trichoscopic Imaging Systems
Advanced microscopic evaluation of the scalp provides crucial clinical information:
Technology Features:
- High-magnification digital imaging of the scalp
- Polarized light systems to reduce reflection
- 3D visualization of follicular units
- Comparative analysis of different scalp regions
Diagnostic Benefits:
- Differentiation between various causes of hair loss
- Detection of scalp conditions that may impact treatment
- Documentation of follicular unit characteristics
- Monitoring of treatment-related changes in follicle size and quality
Non-Surgical Hair Replacement Systems
For those who aren’t candidates for other treatments or prefer non-medical approaches, modern hair systems offer remarkably natural alternatives.
3D-Printed Hair Systems
This technology creates customized non-surgical hair replacement:
Production Process:
- 3D scanning creates an exact model of the client’s scalp
- Computer-assisted design matches the client’s hair pattern and density
- Automated production creates a base that precisely fits the contours of the scalp
- Individual hairs are inserted to match natural growth patterns
Advantages:
- Perfect fit without adhesives or pressure points
- Natural-looking hairline and part
- Customized color matching including multi-dimensional coloring
- Appropriate density for age and facial features
Hybrid Integration Systems
These systems combine a client’s existing hair with supplemental hair:
How They Work:
- Breathable mesh is integrated with the client’s natural hair
- Additional hair is added through the mesh to increase density
- The client’s own hair grows through the system
- Can be styled, washed, and treated like natural hair
Benefits:
- Utilizes the client’s own hairline for completely natural appearance
- No demarcation line between natural and supplemental hair
- Allows for active lifestyles including swimming and sports
- Can be used as a bridge treatment during other hair restoration processes
Virtual Reality Hair Design
Before committing to a treatment, patients can now see potential results:
Process:
- 3D scanning creates a digital model of the patient’s head and existing hair
- Various treatment outcomes are simulated based on different procedures
- Patients can visualize different hairlines, densities, and styles
- Results can be viewed from multiple angles and in different lighting
Applications:
- Setting realistic expectations before procedures
- Comparing different treatment options visually
- Designing optimal hairlines for transplantation
- Assessing the visual impact of different graft numbers and distributions
The Future of Hair Restoration
Research in several areas points to exciting future developments in hair loss treatment.
Cloning and Hair Multiplication
Perhaps the holy grail of hair restoration research is the ability to multiply a patient’s hair follicles:
Current Research:
- Techniques to culture dermal papilla cells from a small donor sample
- Methods to induce these cells to form new follicles when reimplanted
- Research into the signals that control follicular neogenesis
- Studies on maintaining cell properties during laboratory expansion
Potential Impact:
- Would eliminate limitations in donor hair supply
- Could provide unlimited grafts from a small sample
- Would make hair restoration accessible to more patients
- Could potentially restore original hair density
CRISPR and Gene Therapy Approaches
Genetic editing technology might one day address the root causes of hair loss:
Possibilities Being Explored:
- Modification of androgen receptor sensitivity in follicles
- Alteration of inflammatory response genes
- Enhancement of growth factor production
- Promotion of genes associated with prolonged anagen phase
Current Status:
- Primarily in preclinical research stages
- Significant regulatory hurdles remain
- Questions of delivery mechanisms still being addressed
- Ethical considerations being debated
Tissue Engineering for Scarless Procedures
Advanced bioengineering may eliminate many limitations of current approaches:
Emerging Technologies:
- Bioprinting of follicular units with preserved cellular architecture
- Scaffolds that guide follicular regeneration
- Growth factor-infused matrices that support transplanted follicles
- Nanomaterial delivery systems for precise biological signaling
Potential Applications:
- Creation of new follicles without extraction from donor sites
- Regeneration of follicles in scarring alopecias
- Enhanced survival rates for transplanted follicles
- More uniform and predictable results
Choosing the Right Hair Restoration Approach
With so many options available, selecting the appropriate treatment requires careful consideration.
Assessment Factors
Several elements should influence treatment decisions:
Patient-Specific Factors:
- Age and stage of hair loss
- Hair loss pattern and progression rate
- Donor hair characteristics
- Medical history and contraindications
- Lifestyle considerations and recovery time constraints
Treatment-Specific Factors:
- Evidence base for efficacy in similar cases
- Safety profile and potential side effects
- Cost and long-term maintenance requirements
- Combination potential with other treatments
- Provider expertise with the specific technology
The Consultation Process
A comprehensive evaluation should include:
- Detailed medical history review
- Scalp examination with trichoscopy
- Photographic documentation
- Discussion of expectations and limitations
- Review of all available treatment options
- Creation of a customized treatment plan
Managing Expectations
Understanding the realistic outcomes of different treatments is essential:
- Timeline for visible results (varies significantly between approaches)
- Need for maintenance treatments
- Potential for combining multiple technologies
- Importance of addressing underlying causes
- Progression of hair loss despite intervention
Conclusion
The field of hair restoration has entered a truly revolutionary period, with technological advances creating opportunities for more effective, less invasive, and more personalized treatments than ever before. From robotically-assisted surgery to regenerative medicine approaches, the options for addressing hair loss continue to expand rapidly.
For those experiencing hair loss, this evolution means more accessible and effective solutions tailored to individual needs. The stigma once associated with hair restoration is diminishing as results become increasingly natural and detection of procedures nearly impossible. Furthermore, the growing understanding of the psychosocial impact of hair loss has legitimized its treatment as an important aspect of overall wellbeing.
As with any medical field undergoing significant innovation, it’s important to approach newer technologies with appropriate expectations and to seek treatment from qualified providers with specific expertise in the chosen procedures. The most successful outcomes typically result from comprehensive approaches that may combine several complementary technologies, rather than relying on a single intervention.
While the perfect “cure” for baldness remains elusive, the rapid pace of advancement in cosmetic procedures and hair restoration suggests that increasingly effective solutions will continue to emerge. Those affected by hair loss have more reason for optimism than ever before, with options that can be tailored to individual needs, preferences, and goals.